Tiny but mighty: Unlocking the hidden power of 9-amino acid transactivation domains in gene activation
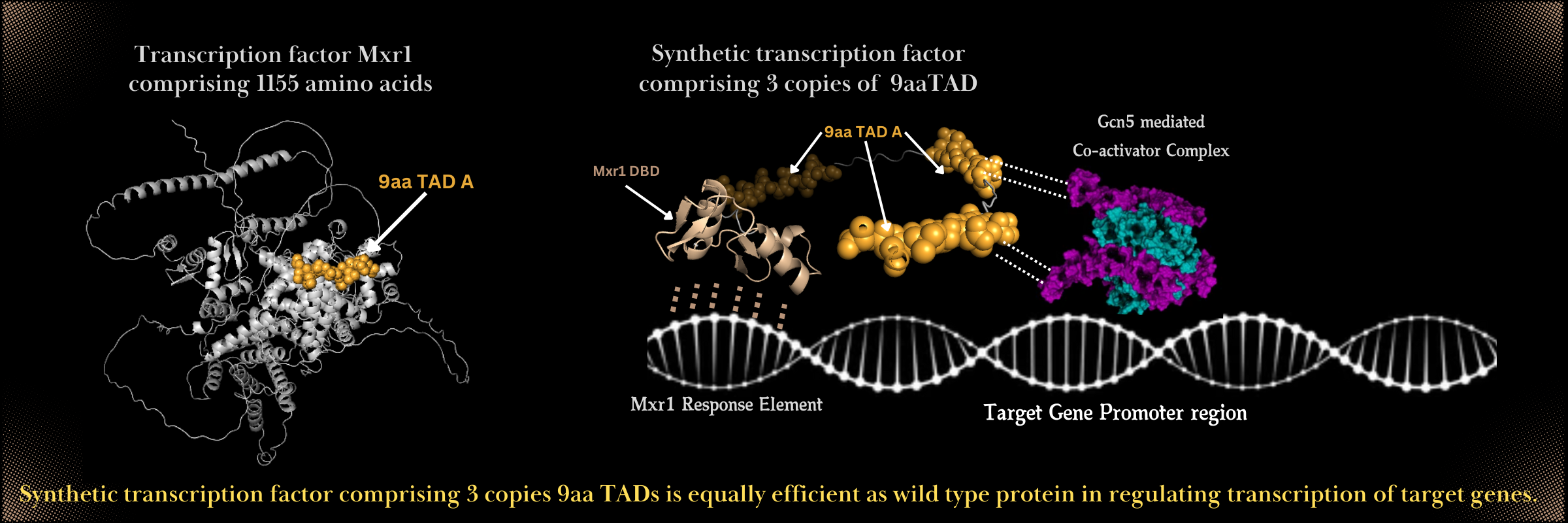
Researchers at the Department of Biochemistry, IISc, led by PN Rangarajan have discovered that tiny segments of a transcription factor (protein) containing just 9 amino acids can independently activate genes in Komagataella phaffii (formerly Pichia pastoris), a yeast widely used in biotechnology. Their study, published in Journal of Biological Chemistry, challenges the belief that large, complex protein segments or structures are needed for gene activation.
The study focuses on Mxr1, a zinc finger transcription factor that controls key metabolic genes in the yeast. The team engineered 21 synthetic transcription factors, each with Mxr1’s DNA-binding domain and three copies of putative 9-amino acid transactivation domains. Remarkably, 11 of these factors successfully restored gene expression in yeast lacking Mxr1 as efficiently as the wild type protein.
These small but potent segments function by recruiting Gcn5, an enzyme that loosens DNA structure, allowing gene activation. This discovery has major implications for biotechnology, particularly for optimising K. phaffii as a host for producing recombinant proteins.
Mxr1 regulates AOX1, a key enzyme in methanol metabolism – its promoter is widely used for high-level protein expression. Harnessing these minimal yet powerful activation domains could lead to development of novel yeast strains for commercial production of vaccines, therapeutic proteins, food additives, and industrial enzymes.
This advancement paves the way for next-generation approaches in synthetic biology and genetic engineering, proving that small molecular tools can drive efficient, scalable biological systems.
REFERENCE:
Priya P, Shivashankar VB, Rangarajan PN, Synthetic transcription factors establish the function of nine amino acid transactivation domains of Komagataella phaffii Mxr1, Journal of Biological Chemistry, (2025).
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021925825000584?via%3Dihub
LAB WEBSITE:
https://biochem.iisc.ac.in/p-n-rangarajan.php




