A novel mouse model of chronic diarrhoea reveals the consequences of fluid-ion imbalance on gut health and functioning
Diarrhoeal diseases are the most common gastrointestinal disorder worldwide. Diarrhoea caused by infection is the second leading cause of death in children under five years of age, with more than 500,000 deaths per annum. Although treatments and preventions for acute diarrhoea are widely available, the long-term consequences of recurrent and chronic diarrhoea, prevalent in developing countries such as India, are not well understood.
In a recent study, researchers led by Prof Sandhya S Visweswariah at the Department of Molecular Reproduction, Development and Genetics developed a novel transgenic mouse model harbouring a rare human mutation initially described in an extended Norwegian family with a history of congenital diarrhoea. The mutation is present in the gene encoding receptor guanylyl cyclase-C (GC-C), the protein receptor for diarrhoea-causing heat-stable enterotoxins secreted by Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. These mice with an activating mutation in GC-C displayed symptoms of diarrhoea such as enhanced faecal water and sodium content, higher frequency of bowel movements, and altered gut motility. Intriguingly, mutant mice showed an altered gut microbiome and expression of genes associated with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). These together predisposed the mouse to experimental colitis. The researchers described an up-regulation of interferon-stimulated genes in the gut, highlighting an altered immune functioning. Therefore, the activating mutation in GC-C resulted in diarrhoea and altered gut physiology, leading to gastrointestinal inflammation.
Preclinical models for diarrhoea are not well established. Therefore, this mouse model provides the first tool to understand the consequences of chronic diarrhoea on the overall health and functioning of the gut. The mouse not only serves as a model for GC-C mediated diarrhoea but will also provide an opportunity to test clinical regimes for the treatment and prevention of diarrhoea and IBD in the future.
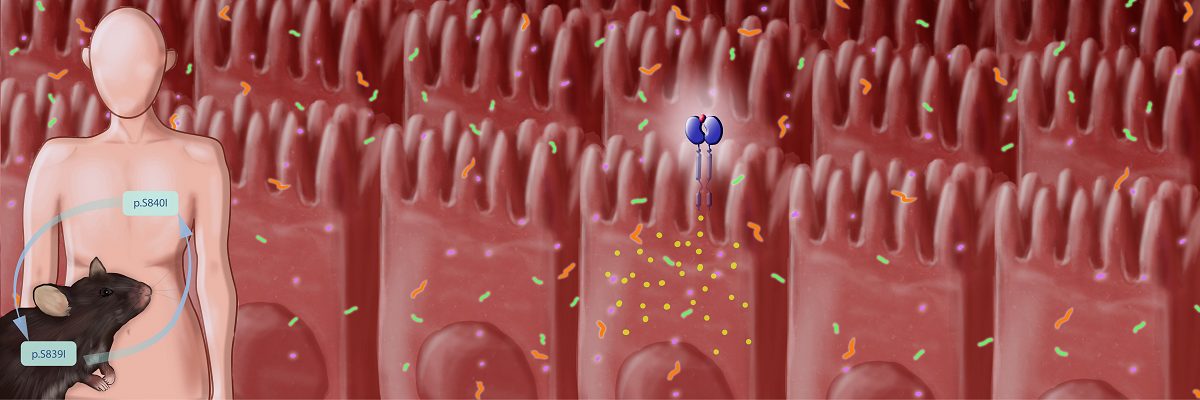
Image: Tejeswani Padma
REFERENCE:
Mishra, V., Bose, A., Kiran, S., Banerjee, S., Shah, I.A., Chaukimath, P., Reshi, M.M., Srinivas, S., Barman, A. and Visweswariah, S.S. (2021) Gut-associated cGMP mediates colitis and dysbiosis in a mouse model of an activating mutation in GUCY2C. J. Exp. Med.
doi: 10.1084/jem.20210479
LAB WEBSITE:
https://sites.google.com/view/sandhya-s-visweswariah/welcome




