Boosting insulin secretion in type 2 diabetes
Diabetes affects around 10% of the Indian population, and its prevalence is increasing in the country at an alarming rate. Current treatments include insulin injections, combinatorial approaches and so on. However, prolonged use of such treatments is associated with various micro and macrovascular complications.
In a new study, researchers from the Department of Developmental Biology and Genetics (DBG), IISc, led by Nikhil R Gandasi, and first author Priyadarshini V, a PhD student, compared the functions of two secretory vesicles in the insulin-producing β-cells of the pancreas.
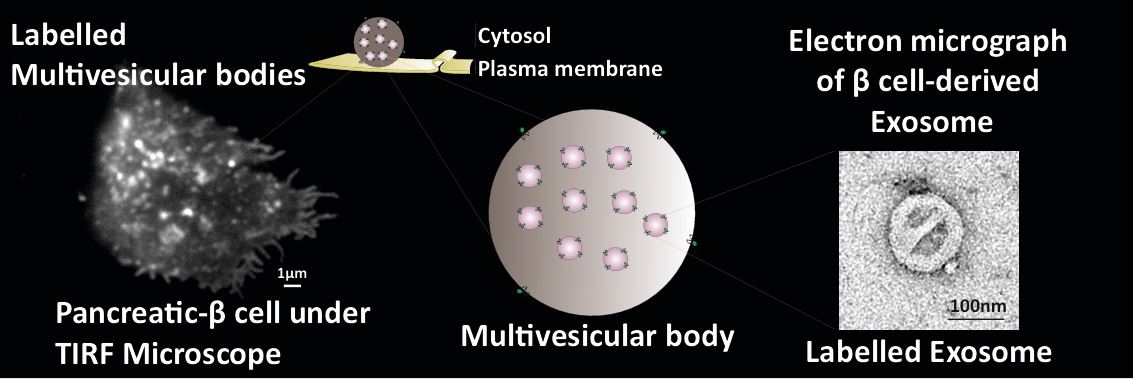
One of the earliest symptoms of type 2 diabetes is losing the ability to secrete insulin, the hormone that reduces blood glucose. In β-cells, insulin is stored in insulin secretory granules (ISGs). In type 2 diabetes, these insulin-producing β-cells form aggregates of islet amyloid polypeptide (fibrillar proteins), which leads to the loss of β-cells, and subsequently reduced insulin secretion. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) secreted from multivesicular bodies (MVBs) during such stress can break the formation of the islet amyloid polypeptide and restore insulin secretion.
Fluorescent tagging of MVBs was validated by transmission electron microscopy by Vidya Mangala Prasad’s lab from Molecular Biophysics Unit (MBU). Fluorescence-based microscopy showed that MVBs were decreased in type 2 diabetic β-cells compared to normal individuals. This showed that loss of insulin secretion in type 2 diabetic β-cells, could also be driven by decrease of MVBs leading to β-cells dysfunction and hence lower number of ISGs.
Moving forward, the researchers plan to use various small molecules to increase EV secretion in order to develop new treatment strategies. This can provide crucial insights for improved management of blood glucose and identifying early diagnosis markers. Further research in this area has the potential to improve insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake in people with diabetes.
REFERENCE:
Veerabhadraswamy P, Lata K, Dey S, Belekar P, Kothegala L, Mangala Prasad V, Gandasi NR,
Comparison of localization and release of multivesicular bodies and secretory granules in islet
cells: Dysregulation during type‐2 diabetes, Journal of Extracellular Biology (2024).
https://doi.org/10.1002/jex2.70014
WEBSITE:
https://dbg.iisc.ac.in/people/nikhil-gandasi/
https://sites.google.com/view/vmprasadlab-iisc/home?authuser=1

Left to right – Lakshmi Kothegala, Kiran Lata, Veerabhadraswamy Priyadarshini, Vidya Mangala Prasad, Nikhil R Gandasi





